(7,781 - 7,800 of 10,079)
Pages
-
-
Title
-
PHOTONASTIC Innovative Facade Technology: L.ROMERO_FINAL_BOARD_1
-
Creator
-
Romero, Loretta
-
Date
-
2012-04-24, 2012-05
-
Description
-
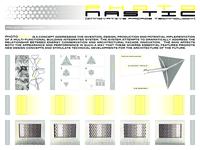
PHOTONASTIC is a concept addressing the invention, design, production and potential implementation of a building integrated system. The system...
Show morePHOTONASTIC is a concept addressing the invention, design, production and potential implementation of a building integrated system. The system attempts to address the relationship between energy conservation and architectural facade innovation. The skin affects both the appearance and performance in such a way that these features promote new design concepts and stimulate technical developments for the architecture of the future.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
PHOTONASTIC Innovative Facade Technology: L_ROMERO_FINAL_BOOK
-
Creator
-
Romero, Loretta
-
Date
-
2012-04-24, 2012-05
-
Description
-
PHOTONASTIC is a concept addressing the invention, design, production and potential implementation of a building integrated system. The system...
Show morePHOTONASTIC is a concept addressing the invention, design, production and potential implementation of a building integrated system. The system attempts to address the relationship between energy conservation and architectural facade innovation. The skin affects both the appearance and performance in such a way that these features promote new design concepts and stimulate technical developments for the architecture of the future.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Fostering Synergy
-
Creator
-
Cooper, Andrea
-
Date
-
2012-05-02, 2012-05
-
Description
-
Fostering Synergy will create a community based support system by pairing young mothers outgrowing the foster care system with community...
Show moreFostering Synergy will create a community based support system by pairing young mothers outgrowing the foster care system with community matriarchs in need of companionship. Each generation has social and physical needs that can be eased through the Fostering Synergy support system.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Fostering Synergy: MasterProject_ACooper-2012
-
Creator
-
Cooper, Andrea
-
Date
-
2012-05-02, 2012-05
-
Description
-
Fostering Synergy will create a community based support system by pairing young mothers outgrowing the foster care system with community...
Show moreFostering Synergy will create a community based support system by pairing young mothers outgrowing the foster care system with community matriarchs in need of companionship. Each generation has social and physical needs that can be eased through the Fostering Synergy support system.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Fostering Synergy: Masters Project Boards_2012AC-final
-
Creator
-
Cooper, Andrea
-
Date
-
2012-05-02, 2012-05
-
Description
-
Fostering Synergy will create a community based support system by pairing young mothers outgrowing the foster care system with community...
Show moreFostering Synergy will create a community based support system by pairing young mothers outgrowing the foster care system with community matriarchs in need of companionship. Each generation has social and physical needs that can be eased through the Fostering Synergy support system.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Monumental Adaptation: Reimagining the Old Chicago Post Office: NT_masters project_final book
-
Creator
-
Turgeon, Noel
-
Date
-
2012-05-01, 2012-05
-
Description
-
MONUMENTAL ADAPTATION: REIMAGINING THE OLD CHICAGO POST OFFICE Built in 1932, the Old Chicago Main Post Office was the largest post office in...
Show moreMONUMENTAL ADAPTATION: REIMAGINING THE OLD CHICAGO POST OFFICE Built in 1932, the Old Chicago Main Post Office was the largest post office in the world at three million square feet. It was designed to accommodate the extension of Congress Parkway and in 1953 the Eisenhower Expressway cut a void through the center of the building. Finally the Post Office was vacated in 1997 and remains unused to this day. This project proposes the adaptation of the Post Office into a hybrid fieldhouse that contains public recreation and retail space. This proposal keeps the Post Office public, utilizing income generated through retail to maintain the building for Chicagoans. Recreation program is inserted into voids carved out of the original building. Retail occupies the peripheral space, surrounding the voids.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Evolution: A holistic rejuvenation and wellness center, Chicago
-
Creator
-
Takle, Rameshwari
-
Date
-
2012-04-24, 2012-05
-
Description
-
My thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design...
Show moreMy thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design as a medium to create a space for an overall holistic experience. I am interested in the ethereal qualities in nature and their ability to tranquilize a person’s state of mind.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Evolution: A holistic rejuvenation and wellness center, Chicago: FINAL PRESENTATION_RTAKLE
-
Creator
-
Takle, Rameshwari
-
Date
-
2012-04-24, 2012-05
-
Description
-
My thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design...
Show moreMy thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design as a medium to create a space for an overall holistic experience. I am interested in the ethereal qualities in nature and their ability to tranquilize a person’s state of mind.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Evolution: A holistic rejuvenation and wellness center, Chicago: Graphic Argument
-
Creator
-
Takle, Rameshwari
-
Date
-
2012-04-24, 2012-05
-
Description
-
My thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design...
Show moreMy thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design as a medium to create a space for an overall holistic experience. I am interested in the ethereal qualities in nature and their ability to tranquilize a person’s state of mind.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
Evolution: A holistic rejuvenation and wellness center, Chicago: RAMESHWARI TAKLE FINAL BOARD
-
Creator
-
Takle, Rameshwari
-
Date
-
2012-04-24, 2012-05
-
Description
-
My thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design...
Show moreMy thesis proposition is to design a center for yoga, meditation and spa. The idea is to engage architecture, hospitality and interior design as a medium to create a space for an overall holistic experience. I am interested in the ethereal qualities in nature and their ability to tranquilize a person’s state of mind.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
The Collegiate Strip: An Urban Renewal of Main Street
-
Creator
-
Wade, Jessica
-
Date
-
2012-04-30, 2012
-
Description
-
This project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed...
Show moreThis project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed site located at the intersection of Jewett Avenue and Main Street provided a new 'Arts Node' where students could live, perform, and practice their given talents. This site also provided a connection to the existing Tri-Main Center which allows public display space for artistic individuals. An infrastructural addition over the existing railway system provided additional outdoor space labeled a 'social alley' that connected Main Street and Jewett Avenue and provided more creative space between the Tri-Main Center and the new Arts Node.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
The Collegiate Strip: An Urban Renewal of Main Street: FinalBoard1
-
Creator
-
Wade, Jessica
-
Date
-
2012-04-30, 2012
-
Description
-
This project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed...
Show moreThis project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed site located at the intersection of Jewett Avenue and Main Street provided a new 'Arts Node' where students could live, perform, and practice their given talents. This site also provided a connection to the existing Tri-Main Center which allows public display space for artistic individuals. An infrastructural addition over the existing railway system provided additional outdoor space labeled a 'social alley' that connected Main Street and Jewett Avenue and provided more creative space between the Tri-Main Center and the new Arts Node.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
The Collegiate Strip: An Urban Renewal of Main Street: FinalBoard2
-
Creator
-
Wade, Jessica
-
Date
-
2012-04-30, 2012
-
Description
-
This project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed...
Show moreThis project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed site located at the intersection of Jewett Avenue and Main Street provided a new 'Arts Node' where students could live, perform, and practice their given talents. This site also provided a connection to the existing Tri-Main Center which allows public display space for artistic individuals. An infrastructural addition over the existing railway system provided additional outdoor space labeled a 'social alley' that connected Main Street and Jewett Avenue and provided more creative space between the Tri-Main Center and the new Arts Node.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
The Collegiate Strip: An Urban Renewal of Main Street: Wade-FinalGraphicArgument
-
Creator
-
Wade, Jessica
-
Date
-
2012-04-30, 2012
-
Description
-
This project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed...
Show moreThis project was a look at redeveloping Main Street in Buffalo,New York to become a new Collegiate Strip for College students. The detailed site located at the intersection of Jewett Avenue and Main Street provided a new 'Arts Node' where students could live, perform, and practice their given talents. This site also provided a connection to the existing Tri-Main Center which allows public display space for artistic individuals. An infrastructural addition over the existing railway system provided additional outdoor space labeled a 'social alley' that connected Main Street and Jewett Avenue and provided more creative space between the Tri-Main Center and the new Arts Node.
Show less
-

-
Title
-
FoodLab - A revitalization strategy for the Pari yard, Sao Paulo - Brazil
-
Creator
-
Lussich Garese, Maria Fernanda
-
Date
-
5/4/2011, 2011-05
-
Description
-
This project aims to develop a new design strategy to redevelop the Pari yard and reclaim the adjacent Tamanduatei river by turning it into an...
Show moreThis project aims to develop a new design strategy to redevelop the Pari yard and reclaim the adjacent Tamanduatei river by turning it into an operative landscape. A holistic system to harverst, clean and reuse the abundant summer rainfall was created in order to enable a highly sustainable urban redevelopment.
Show less
Pages