(9,341 - 9,360 of 10,079)
Pages
-

-
Title
-
Untitled
-
Date
-
1946
-
Description
-
Photograph taken by Mary Henry of a sculpture she made in Nathan Lerner's workshop during her time as a student at the Institute of Design....
Show morePhotograph taken by Mary Henry of a sculpture she made in Nathan Lerner's workshop during her time as a student at the Institute of Design. Inscription on verso: "Mary Henry Photography under Moholy-Nagy. Institute of Design, Chicago. Wire sculpture made in Nathan Lerner's Workshop, I.D."
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Mosaic mural for the First National Bank of San Jose, San Jose, California, detail, ca. 1959
-
Date
-
1959
-
Description
-
Photograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South...
Show morePhotograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South First Street in San Jose, California. Content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Architectural Arts (late 1950s—1964). First National Bank of San Jose (in San Jose?)" Photographer unknown. Date of photograph is unknown. Date listed is approximate.
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Explore Gallery South Wall
-
Date
-
2001
-
Description
-
Drawing of the south wall section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor...
Show moreDrawing of the south wall section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery at the Bellevue Art Museum (now Bellevue Arts Museum) in 2001. Folder-level content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Folder containing announcement of overlapping exhibitions for the opening of the Bellevue Art Museum—her 'North Slope' paintings (never shown together before or since) filling an enormous space on the main floor and 'No Limits,' a 360-degree walk-in mural in the second floor gallery (now obliterated); designs for 'No Limits'; and a review in The Seattle Times."
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Explore Gallery West Wall
-
Date
-
2001
-
Description
-
Drawing of the west wall section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery...
Show moreDrawing of the west wall section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery at the Bellevue Art Museum (now Bellevue Arts Museum) in 2001. Folder-level content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Folder containing announcement of overlapping exhibitions for the opening of the Bellevue Art Museum—her 'North Slope' paintings (never shown together before or since) filling an enormous space on the main floor and 'No Limits,' a 360-degree walk-in mural in the second floor gallery (now obliterated); designs for 'No Limits'; and a review in The Seattle Times."
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Explore Gallery East Wall
-
Date
-
2001
-
Description
-
Drawing of the east wall section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery...
Show moreDrawing of the east wall section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery at the Bellevue Art Museum (now Bellevue Arts Museum) in 2001. Folder-level content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Folder containing announcement of overlapping exhibitions for the opening of the Bellevue Art Museum—her 'North Slope' paintings (never shown together before or since) filling an enormous space on the main floor and 'No Limits,' a 360-degree walk-in mural in the second floor gallery (now obliterated); designs for 'No Limits'; and a review in The Seattle Times."
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Mosaic mural for the First National Bank of San Jose, San Jose, California, ca. 1959
-
Date
-
1959
-
Description
-
Photograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South...
Show morePhotograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South First Street in San Jose, California. Content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Architectural Arts (late 1950s—1964). First National Bank of San Jose (in San Jose?)" Photographer unknown. Date of photograph is unknown. Date listed is approximate.
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-
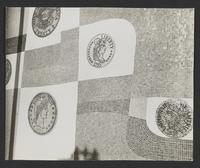
-
Title
-
Mosaic mural for the First National Bank of San Jose, San Jose, California, detail, ca. 1959
-
Date
-
1959
-
Description
-
Photograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South...
Show morePhotograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South First Street in San Jose, California. Content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Architectural Arts (late 1950s—1964). First National Bank of San Jose (in San Jose?)" Photographer unknown. Date of photograph is unknown. Date listed is approximate. Inscription on verso reads "Mary Henry."
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Mosaic mural for the First National Bank of San Jose, San Jose, California, ca. 1959
-
Date
-
1959
-
Description
-
Photograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South...
Show morePhotograph of a mosaic mural created by Mary Henry for the First National Bank of San Jose, constructed ca. 1958 and located at 1010 South First Street in San Jose, California. Content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Architectural Arts (late 1950s—1964). First National Bank of San Jose (in San Jose?)" Photographer unknown. Date of photograph is unknown. Date listed is approximate.
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Detail from Hewlett-Packard mural
-
Description
-
Photograph of a detail from an interior mural painted by Mary Henry at Hewlett-Packard in Palo, Alto, California. Photographer unknown. Date...
Show morePhotograph of a detail from an interior mural painted by Mary Henry at Hewlett-Packard in Palo, Alto, California. Photographer unknown. Date of photograph unknown. Content description from Suzanne Rahn's inventory of the archive: "Professional Architectural Arts Portfolio -- Mounted photos and original drawings of projects: Photographs of the Hewlett Packard mural"
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Repository Refresh: A New Theme for repository.iit
-
Date
-
2016-05
-
Description
-
This year, Illinois Tech's Institutional Repository was given it's first significant visual upgrade since its creation in 2012. The...
Show moreThis year, Illinois Tech's Institutional Repository was given it's first significant visual upgrade since its creation in 2012. The application of a new theme harmonized the repository's look with that of the university and library web sites, added more fluid and natural mobile responsiveness, and brought the repository up to contemporary standards in terms of style and functionality. This poster highlights some of the new features of the new theme, and identify some of the challenges that arose when modifying this theme for use at IIT.
Show less
-
Collection
-
Celebrating Our Successes Mini-Conference 2016
-

-
Title
-
Untitled
-
Date
-
1937-1945
-
Description
-
Untitled photograph by Nathan Lerner depicting a wooden sculpture with smaller shapes casting shadows on a square base. The verso features an...
Show moreUntitled photograph by Nathan Lerner depicting a wooden sculpture with smaller shapes casting shadows on a square base. The verso features an Institute of Design stamp, though it is unknown if this photograph dates from Lerner's time as a student or member of the faculty. Date of photograph unknown. Date listed is approximate.
Show less
-
Collection
-
Institute of Design records, 1937-ca. 1962
-

-
Title
-
Section of No Limits, Bellevue Art Museum, Bellevue, Washington, 2001
-
Date
-
2001
-
Description
-
Photograph of Tara Shaw and Sarah Shaw in front of a section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was...
Show morePhotograph of Tara Shaw and Sarah Shaw in front of a section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery at the Bellevue Art Museum (now Bellevue Arts Museum) in 2001. Based on Henry's designs for the mural, the section depicted appears to be the northwest corner of the room. Inscription on recto: "Part of mural - Bellevue 2001. Tara and Sara Shaw taken by Larry Shaw."
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
-

-
Title
-
Section of No Limits, Bellevue Art Museum, Bellevue, Washington, 2001
-
Date
-
2001
-
Description
-
Photograph of a section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery at the...
Show morePhotograph of a section of No Limits, a 360-degree, walk-in mural designed by Mary Henry that was painted in the second floor gallery at the Bellevue Art Museum (now Bellevue Arts Museum) in 2001. Based on Henry's designs for the mural, the section depicted appears to be the northeast corner of the room. Inscription on recto: "Part of Mural, Bellevue Art Museum 2001."
Show less
-
Collection
-
Mary Dill Henry Papers, 1913-2021
Pages